In electrical and electronic systems, accurate measurement of current is critical for performance, safety, and efficiency. One of the most reliable devices used for this purpose is the precision shunt. But what exactly is a precision shunt? How does it work?
This article explores the basics of precision shunts, their key features, applications, and their importance in industries such as lectric vehicles (EVs), aerospace, telecommunications, and industrial power systems.
I.What is a precision shunt?
A precision shunt (also known as a shunt resistor) is a low-resistance passive device designed to measure current by converting it into a measurable voltage drop. It is placed in series with a circuit and allows current to flow through the circuit while producing a proportional voltage signal (usually in millivolts) that can be read by monitoring equipment.
Key features of precision shunts:
Low resistance value: Minimizes power loss and heat generation.
High accuracy: Provides precise current measurement (usually within ±0.1% or better).
Temperature stability: The use of high-stability alloys such as manganese copper alloy (MnCu) Zeranin and Isotan ensures stable resistance values and reduces the impact of temperature drift.
High power handling: capable of measuring currents from 1A to 12,000A or higher.
Low thermal EMF: prevents measurement errors caused by voltage offsets caused by temperature.
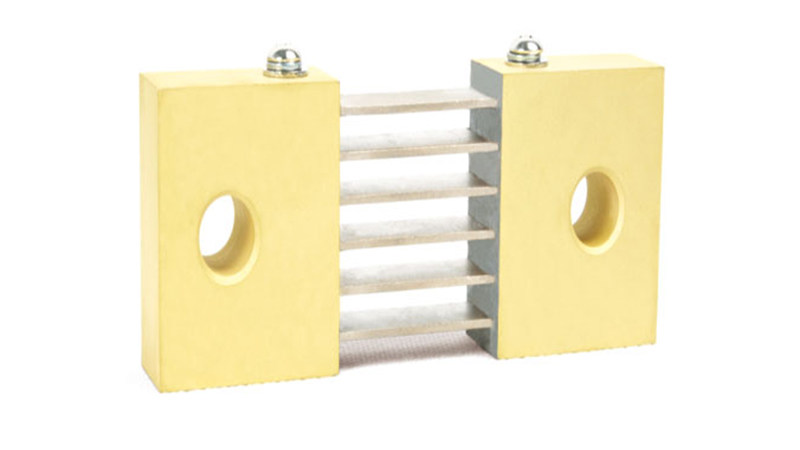
II.The core role of precision shunts
1. Current measurement
The current flowing through the circuit is converted into a proportional voltage signal (such as 50mV, 75mV, 100mV, etc.) through Ohm's law (V = I × R).
Typical accuracy can reach ±0.1% or even higher, suitable for scenarios with strict requirements on measuring current.
2. Low power consumption and low heat generation design
Highly stable alloys such as manganese copper alloy (MnCu) Zeranin and Isotan are used to ensure stable resistance values and reduce the impact of temperature drift.Extremely low resistance (usually milliohms) reduces power loss and avoids system power recovery.
3. Wide range current detection
Can measure currents from 1A to 12,000A or even higher, suitable for a variety of applications from small electronic devices to industrial high current systems.
4. Stable and reliable long-term performance
No stagnation effect, not disturbed by external magnetic fields (magnetic Hall sensor).
Suitable for direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) current measurement, while traditional current transformers (CT) only support AC.
Why use precision shunts instead of other current sensors?
While alternatives such as Hall Effect Sensors and Current Transformers (CTs) exist, precision shunts offer distinct advantages:
| Features | Precision Shunts | Hall Effect Sensors | Current Transformers (CTs) |
| Accuracy | Very High (±0.1%) | Moderate (±1%) | Good (±0.5%) |
| DC/AC Support | Supported (DC and AC) | Supported | Supported | AC Only |
| Linearity | Excellent | Good (magnetic drift) | Good (magnetic drift) | Good |
| Cost | Low to Moderate | High | Moderat |
| Temperature Stability | High | Thermally Affected | Thermally Affected | Stable |
Best suited for:
High-precision DC measurements (e.g., battery systems, EV charging)
High-current applications (e.g., industrial power monitoring)
Cost-sensitive systems that require high accuracy
Applications for Precision Shunts
Dongya precision shunts are widely used for their reliability and accuracy in:
1. Electric Vehicles (EV) and Charging Stations
Measure battery charge/discharge current.
Ensure safe and efficient power delivery for fast charging systems.
2. Renewable Energy and Power Storage
Solar/Wind Inverters.
Battery Management Systems (BMS).
3. Aerospace and Defense
Aircraft Power Distribution.
Satellite and Avionics Current Monitoring.
4. Industrial and Telecom
Data Center Power Supplies.
High-current Rectifiers and UPS Systems.
5. Lab and Test Equipment
Calibration Instruments.
Precision Load Testing.
Choosing the Right Precision Shunt
When choosing a shunt, consider the following:
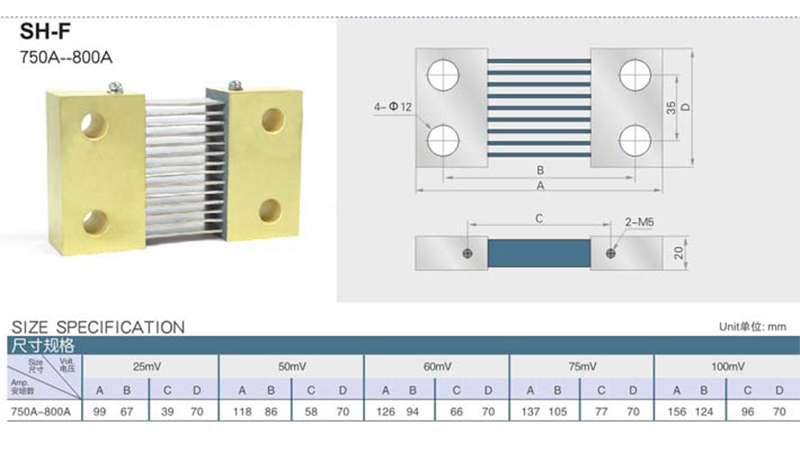
Current range (1A to over 12,000A)
Voltage drop (50mV, 75mV, 100mV, or custom)
Accuracy level (±0.1%, ±0.25%, ±0.5%)
Material (Manganese Bronze, best stability)
Mounting method (PCB, busbar, or bolt-on)
For special needs, we offer custom-designed shunts to meet exact specifications.
Conclusion
Precision shunts are essential for accurate current measurement in high-performance electrical systems. With high accuracy, high stability, and high cost-effectiveness, they are favored in electric vehicles, renewable energy, aerospace, and industrial applications.
For industries that require ultra-precision current sensing, Dongya carefully designed shunts remain one of the most reliable and efficient solutions.
 English
English  한국어
한국어




